The Vanguard S&P 500 Index ETF (VOO) and the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index fund (VTSAX) are two of the largest funds in existence. VOO and VTSAX are the core of many investor portfolios. Many investors compare VTSAX vs VOO in order to decide which should be the foundation of their portfolio.
A quick reminder that this site does NOT provide investment recommendations.
The Short Answer
The main difference between VOO and VTSAX is that VOO is a large- and mid-cap ETF, while VTSAX is a total market mutual fund. Despite these differences, the total return between these two funds is nearly identical and I consider them interchangeable.
I should note that there is an ETF version of VTSAX, which is VTI. Investors looking for an ETF vs ETF comparison should read my review of VTI vs VOO. Readers may also be interested in my standalone VOO review.
The Long Answer
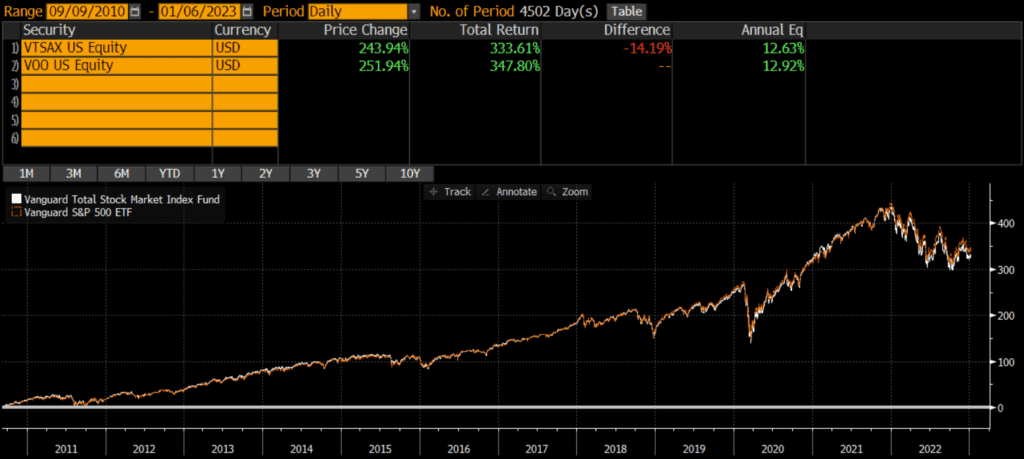
Historical Performance: VTSAX vs VOO
VTSAX was launched on November 13, 2000, while VOO was launched on September 7, 2010. Since then, VOO has outperformed by about .29% annually. This is most likely driven by large-caps’ relative outperformance during this time period, although that dynamic could reverse in the future. That being said, the performance between these two funds is extremely close considering the market cap differences.
Differences between VTSAX vs VOO
The biggest difference between VOO and VTSAX is the market cap exposure of the funds. VOO tracks the S&P 500 index which includes mostly large-caps and some mid-caps, while VTSAX covers much more of the market by including more mid-caps and small-caps.
Geographic Exposure
Both VOO and VTSAX hold essentially 100% stocks, so I will not dig into country exposures or market classification here. For intents and purposes, the two funds have identical exposures.
Market Cap Exposure
VOO focuses on the S&P 500 index and so it mostly holds large-caps with a bit of mid-cap exposure. VTSAX tracks the broader CRSP US Total Market Index and so it owns many more mid-caps and small-caps, as of 10/31/2022. In other words, VOO is a large-cap vehicle, while VTSAX is a total market vehicle. That being said, due to market cap weighting, both funds are overwhelmingly influenced by the large-cap holdings.
| VOO | VTSAX | |
| Large-Cap | 84% | 73% |
| Mid-Cap | 17% | 19% |
| Small-Cap | 0% | 9% |
Sector Weights
The sector weights between VOO and VTSAX are nearly identical, as of 10/31/2022. The weights are within 1% for every single sector.
| VOO | VTSAX | |
| Basic Materials | 2.27% | 2.51% |
| Consumer Cyclical | 10.59% | 10.66% |
| Financial Services | 13.61% | 13.79% |
| Real Estate | 2.74% | 3.45% |
| Communication Services | 7.36% | 6.80% |
| Energy | 5.37% | 5.31% |
| Industrials | 8.69% | 9.64% |
| Technology | 23.60% | 23.06% |
| Consumer Defensive | 7.38% | 6.75% |
| Healthcare | 15.42% | 15.17% |
| Utilities | 2.97% | 2.87% |
Final Thoughts: VTSAX vs VOO
Both VOO and VTSAX are large, core funds sponsored and managed by Vanguard. Although VOO is more of a large-cap ETF and VTSAX is a total market mutual fund, performance has been nearly identical. I view these two funds as essentially interchangeable and would not spend too much energy splitting hairs to decide which one is “better.”
However, there are some situations that may call for one fund versus another.
- Many custodians offer free ETF trades, but charge trading fees or redemption fees for mutual fund. So unless my account was at Vanguard, I might opt for VOO.
- If most of my existing portfolio was mutual funds, I might stick to mutual funds so that settlement periods for trades are consistent (for activities like tax-loss harvesting, etc). Similarly, if most of my portfolio was ETFs, I might stick to ETFs.
- The ETF structure is generally a more tax-efficient vehicle, so VOO may have a lower risk of adverse tax situations in the future. However, Vanguard ETFs are share class of Vanguard mutual funds, so this tax benefit may be muted.
Despite these considerations, these two funds are very similar for all intents and purposes.