The Vanguard Long-Term Corporate Bond Index Fund (Admiral Shares) (symbol VLTCX) and the Vanguard Long-Term Corporate Bond ETF (symbol VCLT) are two of the largest and most popular corporate bond index funds. Some compare VLTCX vs VCLT not realizing that they are just two different share classes of the same portfolio.
A quick reminder that this site does NOT provide investment recommendations. Fund comparisons (such as this one) are not conducted to identify the “best” fund (since that will vary from investor to investor based on investor-specific factors). Rather, these fund comparison posts are designed to identify and distinguish between the fund details that matter versus the ones that don’t.
The Short Answer
VLTCX and VCLT are different share classes of the same portfolio. The decision to buy one or the other depends on investor-specific factors (some of which are listed below).
The Longer Answer
Vanguard ETFs are structured as share classes of their mutual funds. This is a patented structure that is scheduled to expire in 2023, so we may see this structure more frequently in the near future. In other words, VLTCX and VCLT are not two funds pursuing an identical strategy; they are the same fund! Read more about Vanguard’s share class structure and the potential benefits.
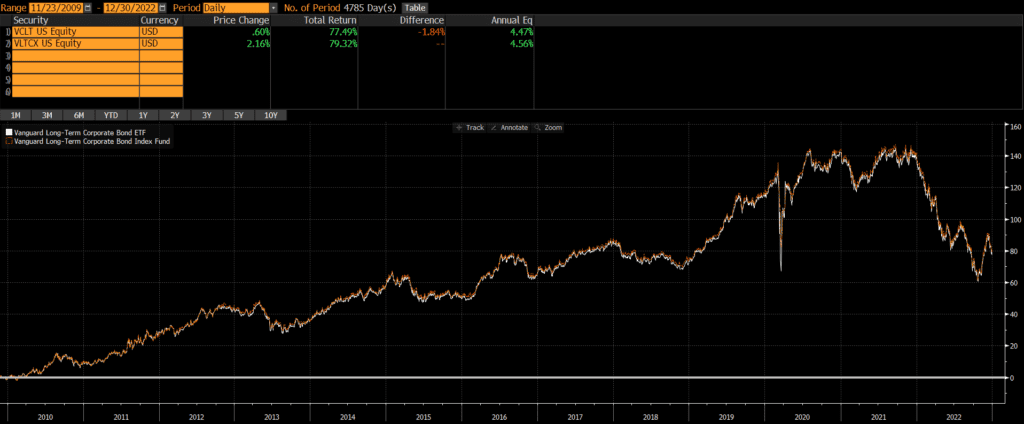
Historical Performance: VLTCX vs VCLT
Both VCLT and VLTCX were launched in late 2009. Not surprisingly, performance has been nearly identical since their common inception date: 4.47% vs 4.56% annually. Despite changes in fees and expenses over that time period, the cumulative difference in performance over that time period is just under 2%! Looking at the chart of VLTCX vs VCLT below, it is obvious that they are identical.
Risks of Fixed-Income ETFs
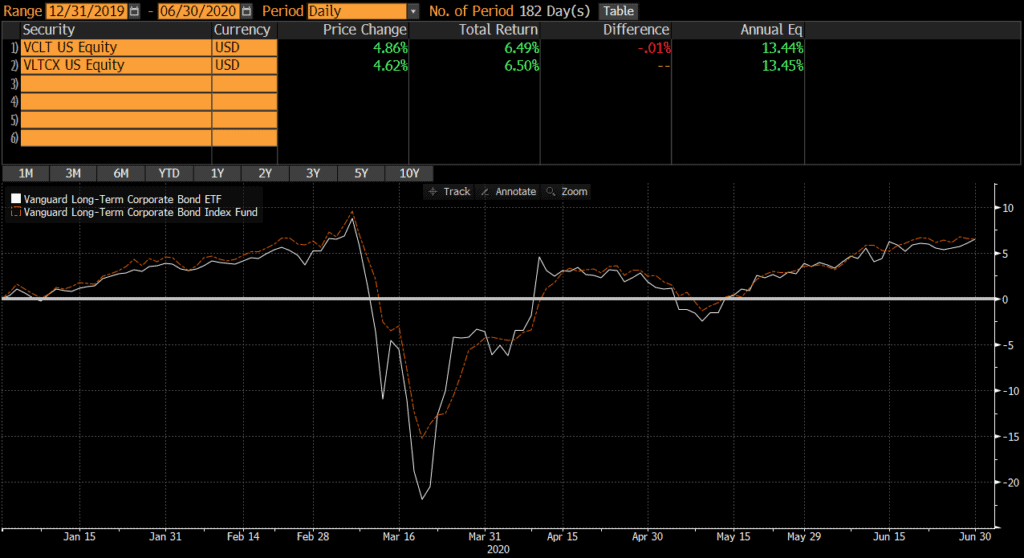
One of the risks of fixed-income ETFs is that they trade well below their net asset value (NAV) in times of distress. This is clear if we chart VLTCX vs VCLT during the first half of 2020. VCLT declined over 30% (peak-to-trough), while VLTCX “only” declined about 25%. Remember, these are simply different share classes of the exact same fund! However, VCLT trades at a market price and VLTCX is traded at a NAV.
This is caused by the fact that fixed-income typically trades at wide bid-ask spreads, which widen even further during market volatility. Sometimes the bids will disappear altogether. Mutual funds generally publish a NAV based on market prices (or estimated values for fixed-income), so estimating a NAV is difficult if the market freezes or bids disappear.
The consensus is that ETFs provide better “price discovery” than mutual funds, since ETFs represent actual market prices. In this example, it is widely assumed that the VCLT value was closer to value of the underlying portfolio than the VLTCX NAV. Interestingly, holders of VLTCX could have sold their holdings and rotated into VCLT (which is the exact same portfolio) at a substantial discount.
Differences Between VLTCX and VCLT
Since the two funds are actually two share classes of the same fund, I will skip the usual comparisons here. The geographic exposures, sector weights, market cap coverage so on is identical because the two funds are shares in the same portfolio. There are some resources on the internet indicating otherwise, but these are incorrect.
Factors to Consider
Transaction Costs
ETFs are free to trade at many brokers and custodians, including Vanguard. However, many brokers and custodians still charge commissions and/or transaction fees to buy/sell mutual funds. To my knowledge, Vanguard does not participate in the pay-to-play arrangements that would allow their mutual funds to trade for free on many platforms. So if an investor account is at Vanguard, it is free to trade VLTCX or VCLT. However, only VCLT is free to trade in non-Vanguard accounts.
Unfortunately, Vanguard does charge a 1% fee on purchases of VLTCX, no matter where the account is held. So investors should consider whether their allocation will be a one-time purchase or averaged in over time, as that may help them determined whether the mutual fund or ETF is a better choice.
There is a bid-ask spread when trading ETFs, but this spread is typically less than .06% for VCLT and individual investor trades will not generally be large enough to “move” the market. In the case of VCLT, individual investors should not have a problem trading.
Tax Efficiency & Capital Gain Distributions
ETFs are typically more tax-efficient than mutual funds, due to their ability to avoid realizing capital gains through like-kind redemptions (a process that is beyond the scope of this post). However, since Vanguard ETFs are a share class of their mutual funds, the mutual funds are able to benefit from this feature of the ETF. In other words, VCLT is able to extend its tax benefits to VLTCX.
One additional consideration is that fixed-income ETFs are not quite as tax-efficient as equity ETFs. Both VLTCX and VCLT have made a capital gains distributions in the past. I noticed some posts on the internet saying that VCLT is more tax-efficient than VLTCX, but this incorrect.
Tax Loss Harvesting
My personal preference is to keep a portfolio entirely mutual funds or entirely ETFs, due to the mechanics of settlement during tax loss harvesting. If an ETF has declined in value and an investor sells it, the trade and cash proceeds will not settle for two business days (T+2). That investor may want to “replace” the sold ETF immediately and attempt to buy another ETF or mutual fund simultaneously.
However, mutual funds settle on T+1 basis, so cash for the mutual purchase would be due in one business day (which is one day earlier than the cash from the ETF sale is received). This can obviously cause problems and (even though this issue can be addressed with careful planning) I find it easier to keep accounts invested in similar vehicles. In this case, if a portfolio is all mutual funds, I might lean more towards VLTCX. If all ETFs, I might lean more towards VCLT.
On this topic, investors should probably avoid using these two funds as tax loss harvesting substitutes for one another since they would likely be considered “substantially identical.”
Tradability
VLTCX does have a stated minimum initial purchase of $3,000, so that may be a factor for some investors looking to initiate a position. The minimum purchase size for VCLT is typically one share, although fractional shares are becoming more common.
Investors can trade ETFs intraday, as well as in the pre-market and after-hours trading sessions. Investors can only buy/sell mutual funds once per day. This is not necessarily a major factor for long-term investors however.
Final Thoughts: VLTCX vs VCLT
VLTCX and VCLT are literally the same portfolio. However, I personally shy away from fixed-income ETFs due to their tendency to trade below NAV during episodes of extreme volatility. If two options provide the same risk and return, but one does not have periodic blowups then I’ll go with that one. Of course, there are other factors to consider (such as the above).