The Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) and the iShares Core S&P 500 ETF (IVV) are two of the largest S&P 500 ETFs and are sponsored by Vanguard and Blackrock respectively. VOO and IVV are a core holding of many investor portfolios and many investors compare VOO vs IVV in order to decide which should be the foundation of their portfolio.
The Short Answer
VOO and IVV identical in nearly every way and risk/return between these two funds is nearly identical and I consider them interchangeable.
A quick reminder that this site does NOT provide investment recommendations. Fund comparisons (such as this one) are not conducted to identify the “best” fund (since that will vary from investor to investor based on investor-specific factors). Rather, these fund comparison posts are designed to identify and distinguish between the fund details that matter versus the ones that don’t.
The Long Answer
Historical Performance: IVV vs VOO
IVV was launched back in 2000, while IVV was launched a decade later in September 2010. Since then, performance has been identical with VOO outperforming by .02% annually. The cumulative performance differential over the past decade plus is less than 1%!
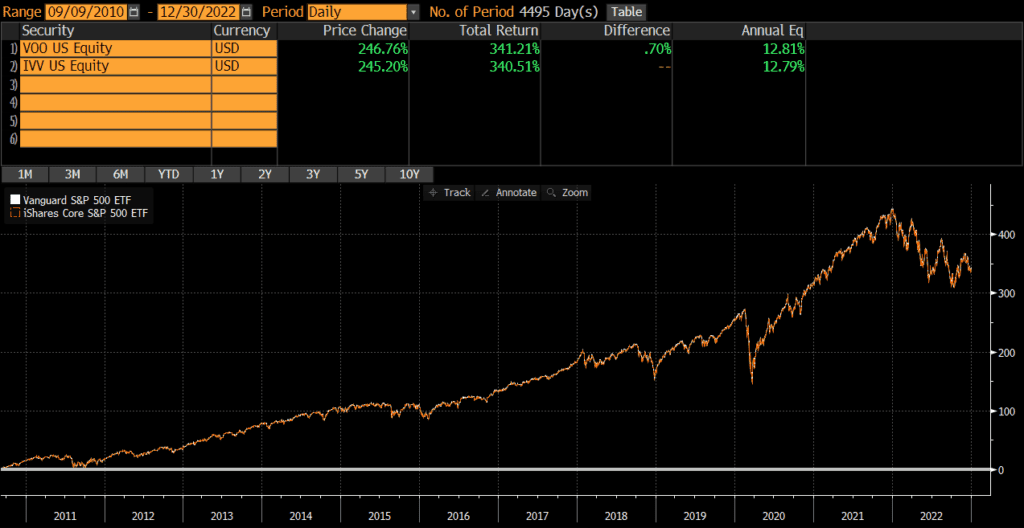
Differences between IVV vs VOO
These two funds track the same S&P 500 index and so there are almost no differences between the funds.
Geographic Exposure
Both VOO and IVV hold essentially 100% US stocks, so I will not dig into country exposures or market classification here. For all intents and purposes, the two funds have identical exposures.
Market Cap Exposure
Again, I won’t dig into market cap exposures since they are identical for IVV and VOO.
Sector Weights
VOO and IVV sector weights are also identical.
Expenses
Both funds have an expense ratio of .03%, which is extremely low.
Transaction Costs
ETFs are free to trade at many brokers and custodians, so both VOO and IVV should be free to trade in most cases. Additionally, these funds are among the largest ETFs and are very liquid. The bid-ask spread of both VOO and IVV is about .01%, so individual investor trades will not generally be large enough to “move” the market.
Tax Efficiency & Capital Gain Distributions
ETFs are typically more tax-efficient than mutual funds, due to their ability to avoid realizing capital gains through like-kind redemptions (a process that is beyond the scope of this post). VOO has never made a capital gains distribution and IVV has not made a capital gains distribution since 1996 (and I do not expect it to moving forward). Thus, these funds are about as tax-efficient as any fund can be and either fund is appropriate in taxable accounts.
Options Strategies
Neither VOO nor IVV has a great options market, despite their enormous AUM. Investors looking to integrate options strategies into their S&P 500 exposure may want to look at SPY. It is more expensive than VOO or IVV, but it has the most liquid options of any ETF. Those interested should read my reviews of IVV vs SPY or VOO vs SPY.
Final Thoughts: IVV vs VOO
Both VOO and IVV are large, core funds sponsored and managed by two of the largest investment sponsors in the world. I view these two funds as essentially interchangeable and would not spend too much energy splitting hairs to decide which one is “better.” In my opinion, both funds are among the best S&P 500 ETFs out there and investors cannot really go wrong with either.